1.Index
索引支持在MongoDB中高效地执行查询。如果没有索引,MongoDB必须执行全集合扫描,即扫描集合中的每个文档,以选择与查询语句匹配的文档。这种扫描全集合的查询效率是非常低的,特别在处理大量的数据时,查询可以要花费几十秒甚至几分钟,这对网站的性能的影响非常巨大。
如果查询存在适当的索引,MongoDB可以使用该索引限制必须检查的文档数。
索引是特殊的数据结构,它以易于遍历的形式存储集合数据集的一小部分。索引存储特定字段或一组字段的值,按字段值排序。索引项的排序支持有效的相等匹配和基于范围的查询操作。此外,MongoDB还可以使用索引中的排序返回排序结果。
2.索引的类型
(1) 单字段索引
MongoDB支持在文档的单个字段上创建用户定义的升序/降序索引,称为单字段索引(Single Field Index)。
对于单个字段索引和排序操作,索引键的排序顺序(即升序或降序)并不重要,因为MongoDB可以在任何方向上遍历索引。
(2) 复合索引
MongoDB还支持多个字段的用户定义索引,即复合索引(Compound Index)
复合索引中列出的字段顺序具有重要意义。例如,如果复合索引由 { userid: 1, score: -1 } 组成,则索引首先按userid正序排序,然后在每个userid的值内,再在按score倒序排序
(3) 其他索引
- 地理空间索引(Geospatial Index)
为了支持对地理空间坐标数据的有效查询,MongoDB提供了两种特殊的索引:返回结果时使用平面几何的二维索引和返回结果时使用球面几何的二维球面索引。
- 文本索引(Text Indexes)
MongoDB提供了一种文本索引类型,支持在集合中搜索字符串内容。这些文本索引不存储特定于语言的停止词(例如“the”、“a”、“or”),而将集合中的词作为词干,只存储根词。
- 哈希索引(Hashed Indexes)
为了支持基于散列的分片,MongoDB提供了散列索引类型,它对字段值的散列进行索引。这些索引在其范围内的值分布更加随机,但只支持相等匹配,不支持基于范围的查询。
3.索引的查看
语法:
1
| > db.[collection_name].getIndexes()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| > db.my_comment.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2, // 索引引擎的版本号
"key" : { // 索引是建立在哪些字段上
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_", // 索引名称
"ns" : "articledb.my_comment" // 索引的 namespace
}
]
|
结果中显示的是默认 _id 索引。
默认 _id 索引:
MongoDB 在创建集合的过程中,在 _id 字段上创建一个唯一的索引,默认名字为 _id_,该索引可防止客户端插入两个具有相同值的文档,不能在 _id 字段上删除此索引。
注意:该索引是唯一索引,因此值不能重复,即 _id 值不能重复的。在分片集群中,通常使用 _id 作为片键。
4.索引的创建
语法:
1
| > db.[collection_name].createIndex({[keys]}, {[options](可选)})
|
options:
|Parameter|Type|Description|
|-|-|-|
|unique|boolean|建立的索引是否唯一。指定为true创建唯一索引。默认值为false.|
|name|string|索引的名称。如果未指定,MongoDB的通过连接索引的字段名和排序顺序生成一个索引名称。|
(1) 创建单字段索引
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| > db.my_comment.createIndex({"userid": 1}) // 1: 升序,-1: 降序
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.my_comment.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "articledb.my_comment"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"userid" : 1
},
"name" : "userid_1",
"ns" : "articledb.my_comment"
}
]
|
(2) 创建复合索引
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
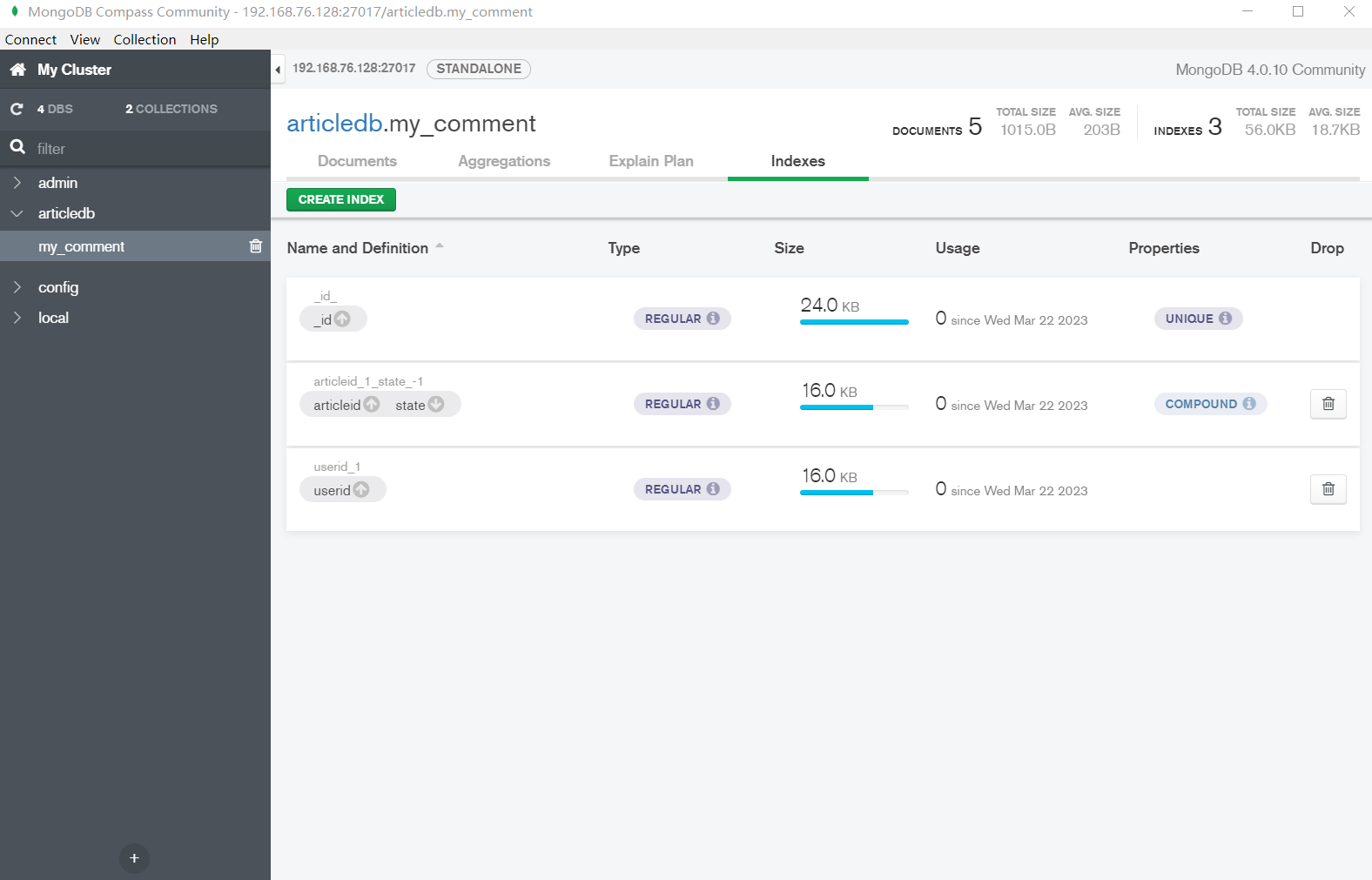
| > db.my_comment.createIndex({"articleid": 1, "state": -1})
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 2,
"numIndexesAfter" : 3,
"ok" : 1
}
>
> db.my_comment.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "articledb.my_comment"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"userid" : 1
},
"name" : "userid_1",
"ns" : "articledb.my_comment"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"articleid" : 1,
"state" : -1
},
"name" : "articleid_1_state_-1",
"ns" : "articledb.my_comment"
}
]
|
在 Compass 中查看
5.索引的移除
语法:
1
| > db.[collection_name].dropIndex([index])
|
index:
|Parameter|Type|Description|
|-|-|-|
|index|string or document|指定要删除的索引。可以通过索引名称或索引规范文档指定索引。若要删除文本索引,请指定索引名称。|
(1) 根据索引名称删除
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| > db.my_comment.dropIndex("userid_1")
{ "nIndexesWas" : 3, "ok" : 1 }
> db.my_comment.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "articledb.my_comment"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"articleid" : 1,
"state" : -1
},
"name" : "articleid_1_state_-1",
"ns" : "articledb.my_comment"
}
]
|
(2) 根据索引规范文档删除
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| > db.my_comment.dropIndex({"articleid": 1, "state": -1})
{ "nIndexesWas" : 2, "ok" : 1 }
> db.my_comment.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "articledb.my_comment"
}
]
|
(3) 删除所有索引
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| > db.my_comment.dropIndexes()
{
"nIndexesWas" : 1,
"msg" : "non-_id indexes dropped for collection",
"ok" : 1
}
> db.my_comment.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "articledb.my_comment"
}
]
|
提示: _id 的字段的索引是无法删除的,只能删除非 _id 字段的索引。
6.执行计划
分析查询性能(Analyze Query Performance)通常使用执行计划(解释计划、Explain Plan)来查看查询的情况,如查询耗费的时间、是
否基于索引查询等。
那么,通常,我们想知道,建立的索引是否有效,效果如何,都需要通过执行计划查看。
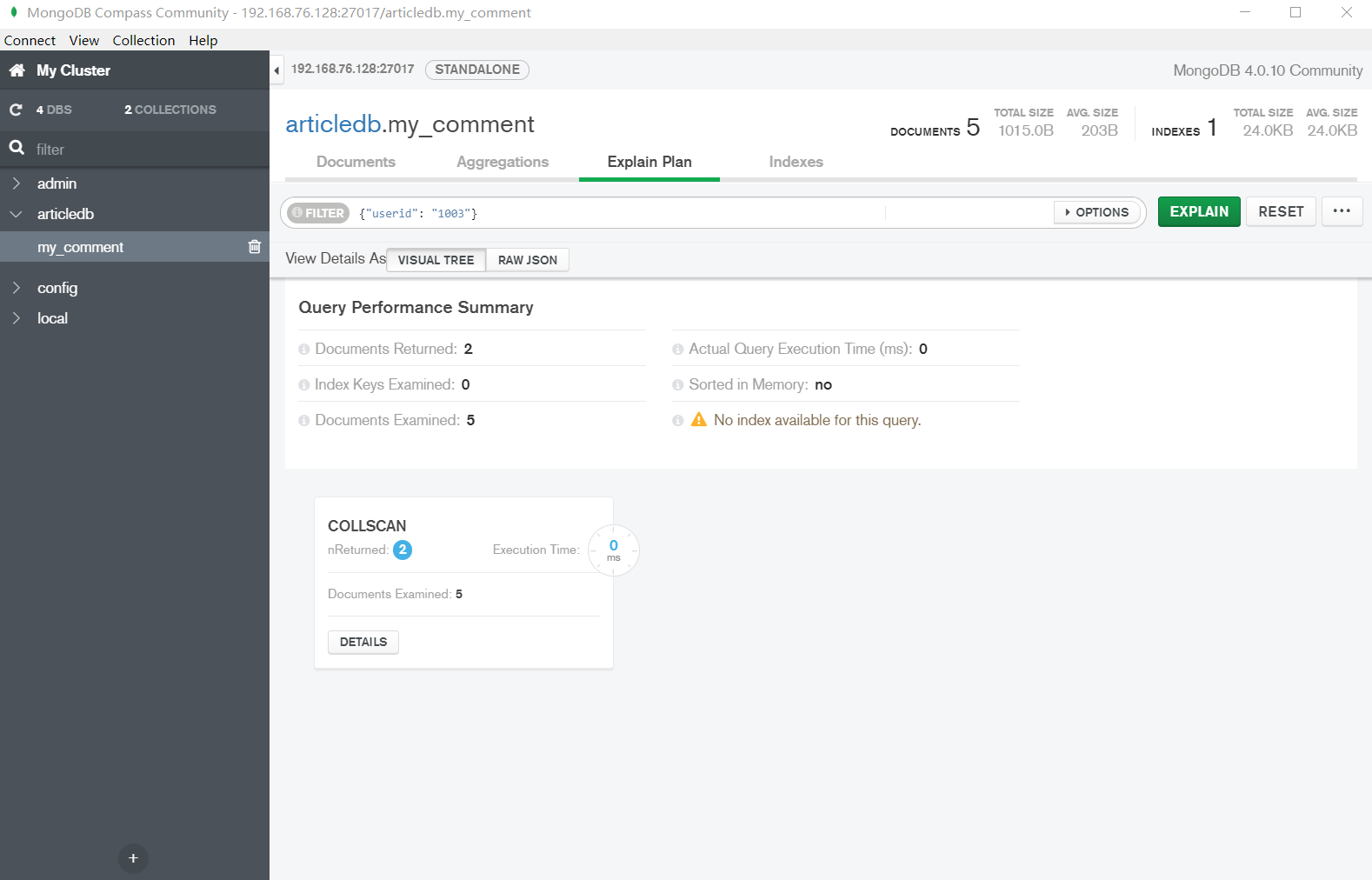
(1) 未使用索引进行查询
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| > db.my_comment.find({"userid": "1003"}).explain()
{
"queryPlanner" : {
"plannerVersion" : 1,
"namespace" : "articledb.my_comment",
"indexFilterSet" : false,
"parsedQuery" : {
"userid" : {
"$eq" : "1003"
}
},
"winningPlan" : {
"stage" : "COLLSCAN", // 全集合扫描
"filter" : {
"userid" : {
"$eq" : "1003"
}
},
"direction" : "forward"
},
"rejectedPlans" : [ ]
},
"serverInfo" : {
"host" : "localhost.localdomain",
"port" : 27017,
"version" : "4.0.10",
"gitVersion" : "c389e7f69f637f7a1ac3cc9fae843b635f20b766"
},
"ok" : 1
}
|
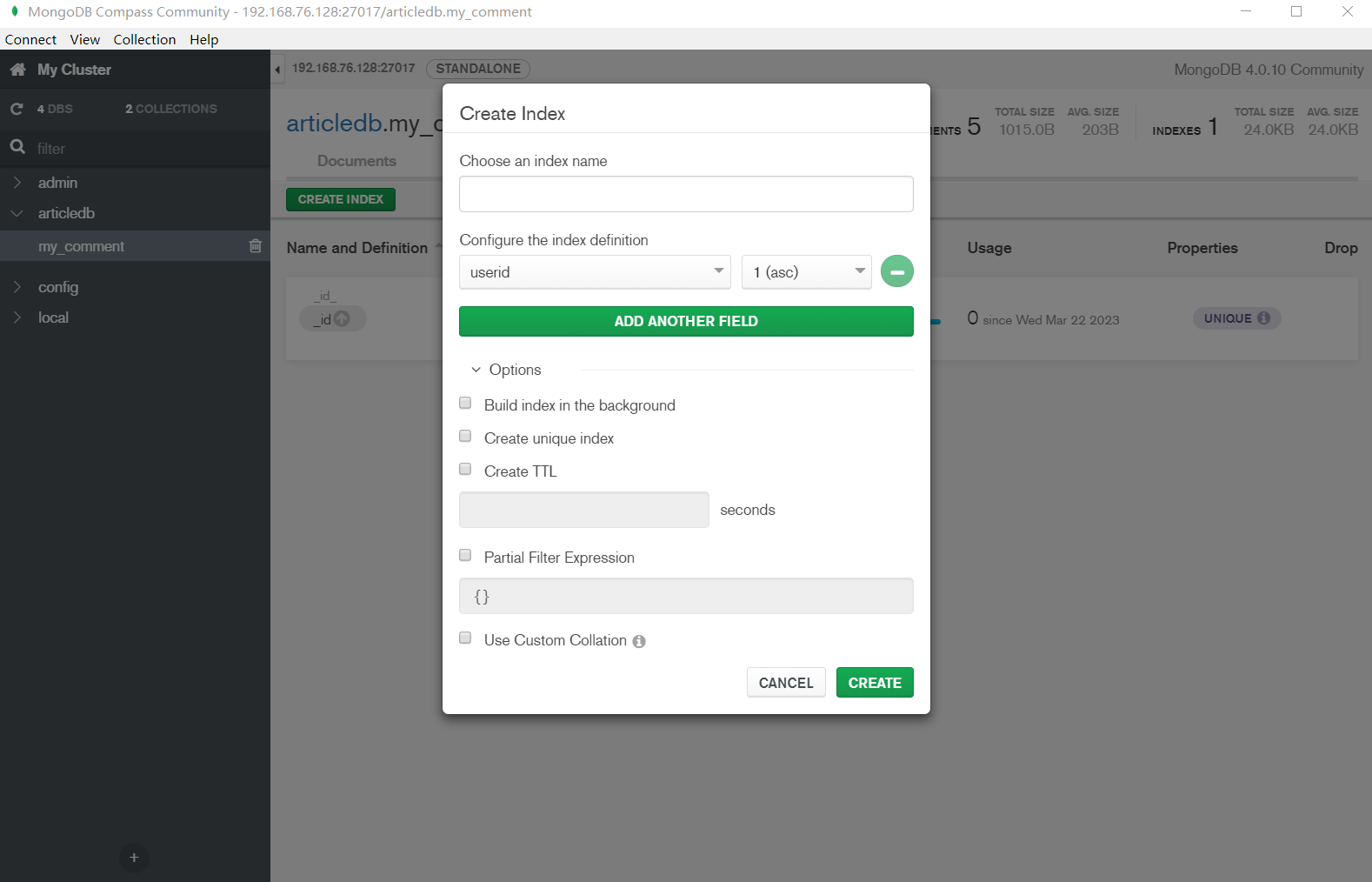
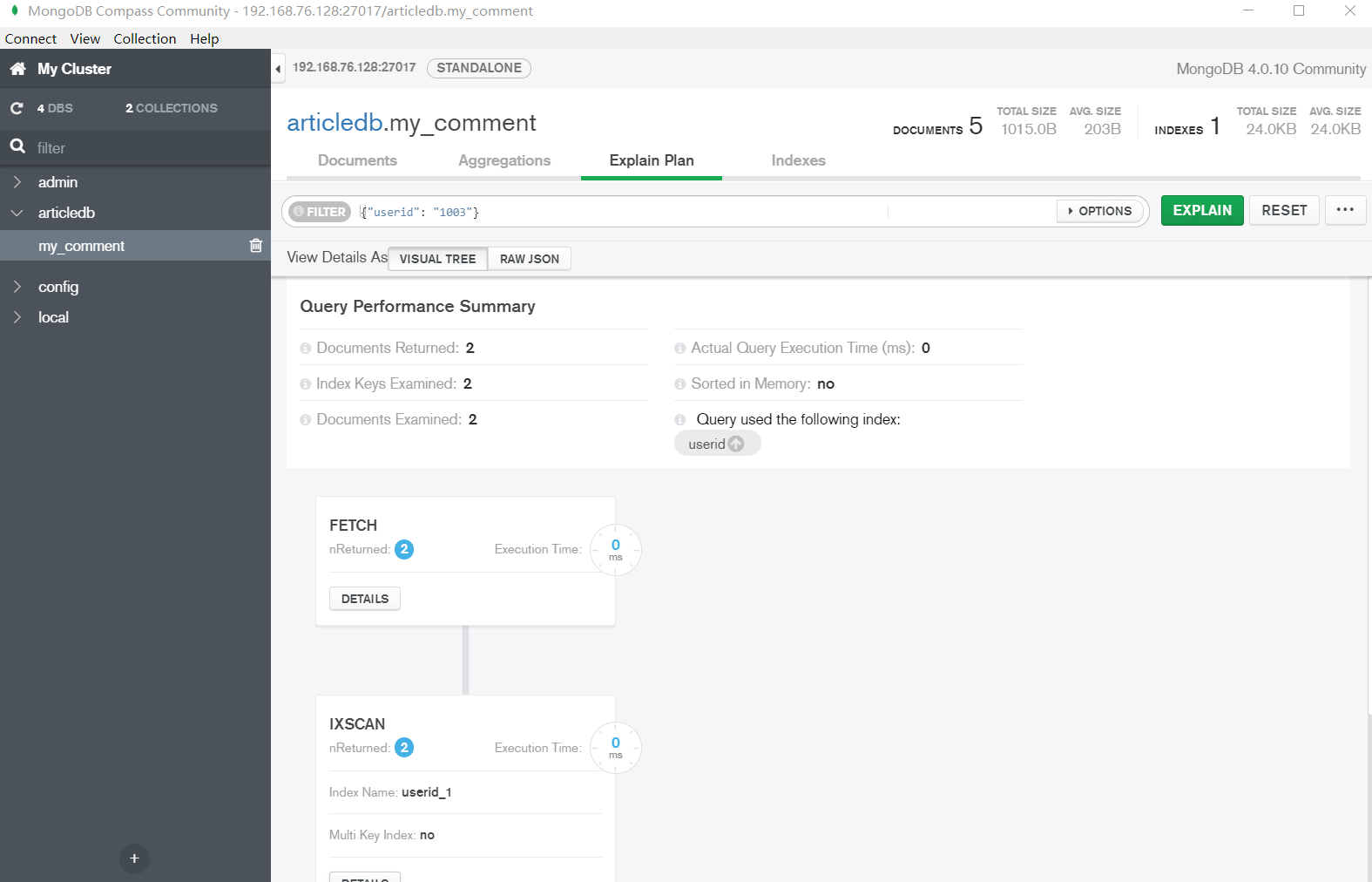
(2) 使用索引进行查询
创建索引:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| > db.my_comment.find({"userid": "1003"}).explain()
{
"queryPlanner" : {
"plannerVersion" : 1,
"namespace" : "articledb.my_comment",
"indexFilterSet" : false,
"parsedQuery" : {
"userid" : {
"$eq" : "1003"
}
},
"winningPlan" : {
"stage" : "FETCH",
"inputStage" : {
"stage" : "IXSCAN", // 基于索引的扫描
"keyPattern" : {
"userid" : 1
},
"indexName" : "userid_1",
"isMultiKey" : false,
"multiKeyPaths" : {
"userid" : [ ]
},
"isUnique" : false,
"isSparse" : false,
"isPartial" : false,
"indexVersion" : 2,
"direction" : "forward",
"indexBounds" : {
"userid" : [
"[\"1003\", \"1003\"]"
]
}
}
},
"rejectedPlans" : [ ]
},
"serverInfo" : {
"host" : "localhost.localdomain",
"port" : 27017,
"version" : "4.0.10",
"gitVersion" : "c389e7f69f637f7a1ac3cc9fae843b635f20b766"
},
"ok" : 1
}
|
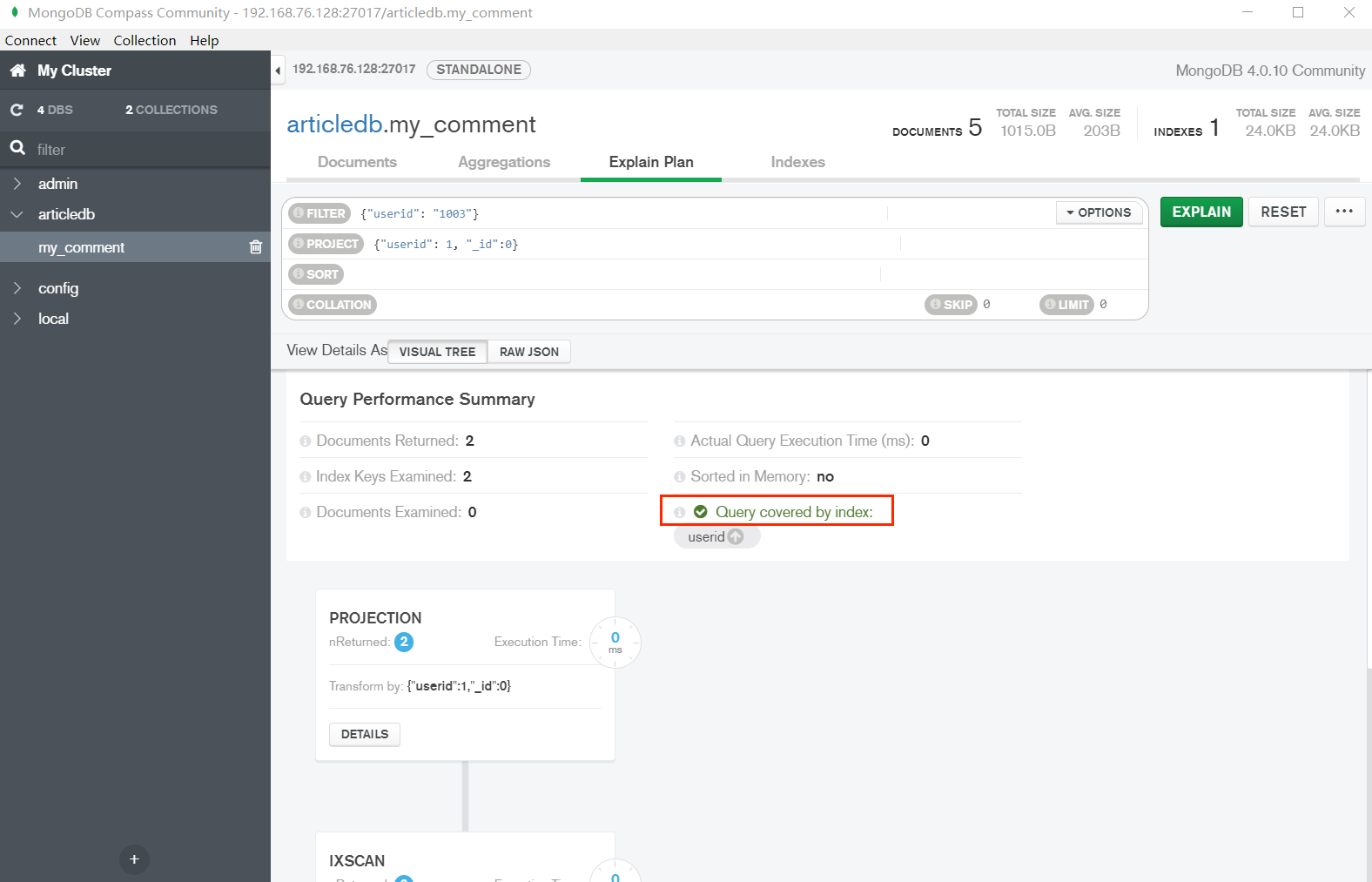
7.涵盖的查询(Covered Queries)
当查询条件和查询的投影仅包含索引字段时,MongoDB直接从索引返回结果,而不扫描任何文档或将文档带入内存。这些覆盖的查询可以非常高效。